Language
Cilico are Committed to Becoming the World's
Leading Solution Provider of IOT Application Technology
23 Years Focus on PDA, Selling in 80 Countries Around the World
Cooperation with More than 5,000 Well-known Companies Worldwide
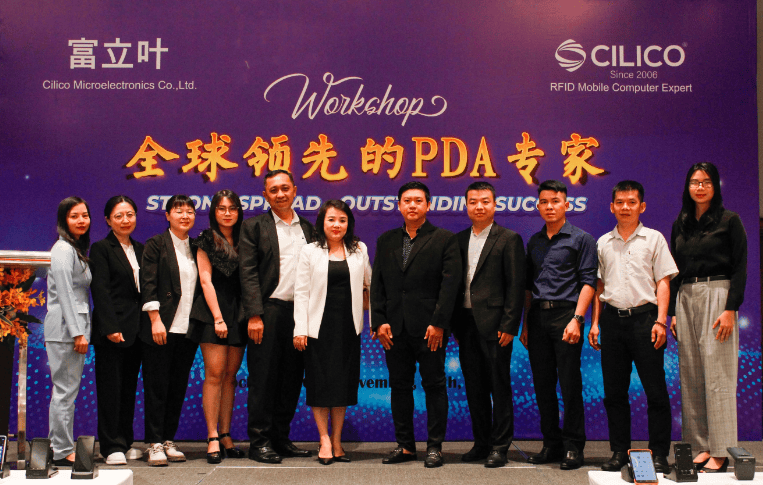
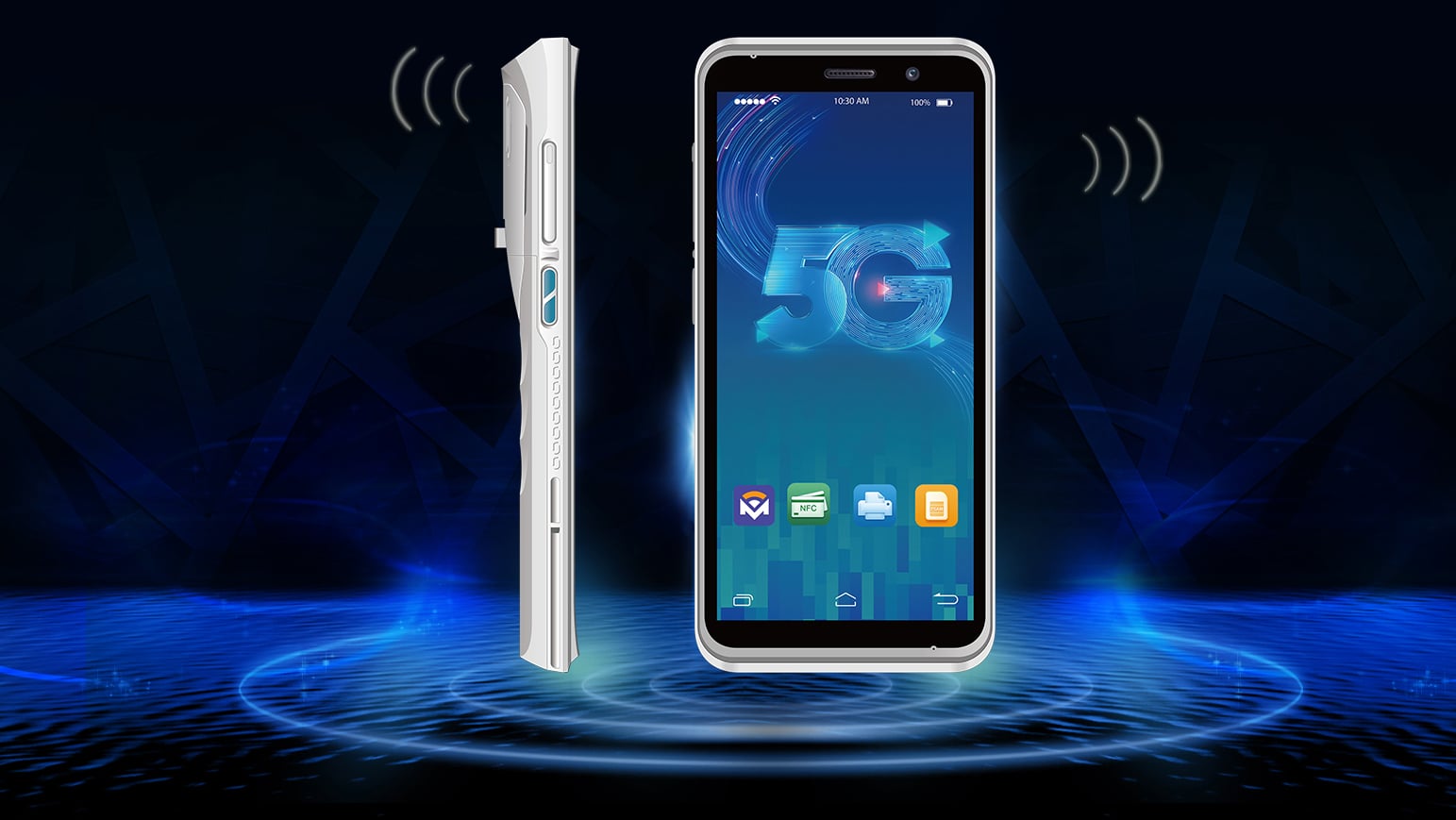
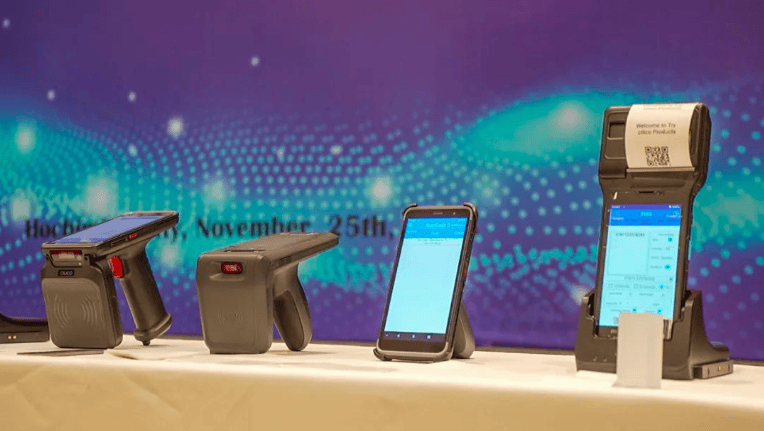









Founded in 2006, Headquartered in Xi' an, ClLlCO Microelectronics Ltd. has set up its sales offices in Shenzhen, Hangzhou, Chengdu and Hongkong. The company also has a supply chain management team and manufacturing facilities in Shenzhen. For future development, the company has already bought its own office in Xi' an National High-tech Development Zone , a 3-floor building with 3000 square meters working space.





CILICO
Becoming the Leading IOT Enterprise


Email:contact@cilico.com
